Gingivitis is the most common form of periodontal disease and can be reversed if caught and treated early. If left untreated, it is a serious problem that can lead to tooth loss and other health problems. However, many people do not seek gingivitis treatment until it has progressed to a more serious stage.
At TEETH @ Tiong Bahru, we focus on treating and preventing gingivitis and all forms of periodontal disease. Our team of dentists are experienced in using the latest techniques and technologies to reverse the effects of gingivitis and help you maintain your oral health for life.
What Should You Know about Gingivitis?
Our teeth go deeper into our gums than we can see. Where they connect, there is a small space where debris or bacteria can accumulate. If good oral hygiene is not maintained, bacteria builds up, increasing the likelihood of infection and gingivitis.
Acute and chronic gingivitis is a common disease that afflicts gums. It’s easy to tell healthy gums vs gingivitis. When the gums are affected, they become swollen, tender, and irritated. Over time, this can develop into worse dental conditions. Infection often occurs because of poor oral hygiene, accumulating undesired bacteria in the mouth.
Gingivitis is a very treatable disease, but like most afflictions, it is better to aim for prevention with a rigorous daily dental health routine. If you have developed gingivitis, treat the condition quickly before it develops into a more serious condition, like periodontitis.
What Are the Symptoms of Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
Swollen, red gums that bleed easily are signs of gingivitis. Gingivitis can progress into more serious periodontal disease, characterized by a buildup of dental plaque and calculus on the teeth, also known as tartar. Gum recession and swollen, bright red gums are common symptoms of periodontal disease and periodontitis.
Symptoms of gingivitis and signs of gum disease include:
- Your gums becoming red, sensitive, swollen, or start to bleed when you brush or floss your teeth
- Gums peeling away from your teeth, causing your teeth to become loose
- Change in how your teeth fit together when you bite (malocclusion)
- Partial dentures that don’t fit, creating pain when biting
- Persistent bad breath that does not go away even after brushing your teeth
If you’re looking to find out how to cure gingivitis, you will need to know the causes and measures to prevent the condition with periodontitis treatment.
What Causes Gingivitis?
Poor oral hygiene is the most common gingivitis and gingival recession cause. However, gingivitis can also strike people who maintain a good dental regimen. Researchers have found that hormonal changes, like those caused by pregnancy, increase the risk of gum inflammation. Additionally, crowded or overlapping teeth make maintaining dental hygiene difficult, as areas in the mouth are difficult to brush or floss. Other common factors include diabetes, certain drugs, tobacco use, a poor diet, and hereditary predisposition.

Periodontal disease, on the other hand, starts from gingivitis itself. It is also influenced by other factors but is primarily caused by gingivitis. This means periodontal disease is within a patient’s control, as long as they work towards preventing gingivitis and treating infections and gum problems as and when they arise.
Some varieties of gingivitis-causing swollen gums aren’t caused by plaque buildup. They may be caused by certain medications, viruses, or fungi, such as thrush, an impacted tooth, or a tooth that hasn’t fully emerged. In the last case, the flap of gum over the tooth can trap debris and cause gingivitis.
Gingivitis Prevention
Severe periodontitis affects over 11% of adults and is a significant cause of tooth loss, impacts negatively upon speech, nutrition, quality of life, and self-esteem, and has systemic inflammatory consequences.
Periodontitis is a prevalent and irreparable inflammatory condition and represents a significant concern for public health. It is preventable, and treatment leads to reduced rates of tooth loss and improved quality of life. Successful gingival swelling treatment necessitates behaviour change in patients to address lifestyle risk factors (e.g., smoking) and – most importantly – to attain and sustain lifelong high standards of daily plaque removal.
While mechanical plaque removal remains the bedrock of successful periodontal disease management, the critical threshold for plaque accumulation to trigger periodontitis is low in high-risk patients. Such patients may benefit from adjunctive agents for the primary prevention of periodontitis.
Treatment of Gingivitis
Unfortunately, the gingival recession cannot be reversed. The goal of gingivitis treatment is to maintain good oral hygiene and stop any additional damage from occurring.
If you smoke, work on cutting back as much as possible as an initial step towards the treatment of gingival recession. Degradation of gum tissue strength is caused by harmful compounds in tobacco that increase the risk of the need to get gingival recession treatment.
Damaged tissue will not grow back, but there are specific dental hygiene steps to keep the gums from receding more. The first treatment step in a gingivitis remedy is deep cleaning the affected area to remove debris. Using an ultrasonic scaler, your dentist will remove any plaque or hardened tartar that you would not be able to remove at home.
Scaling is critical to the cleaning process, as your dentist will safely remove the accumulated plaque on your gum line. Some patients with more severe gum deterioration may opt for local anaesthetic for the scaling process, as periodontal disease makes the gums more sensitive.
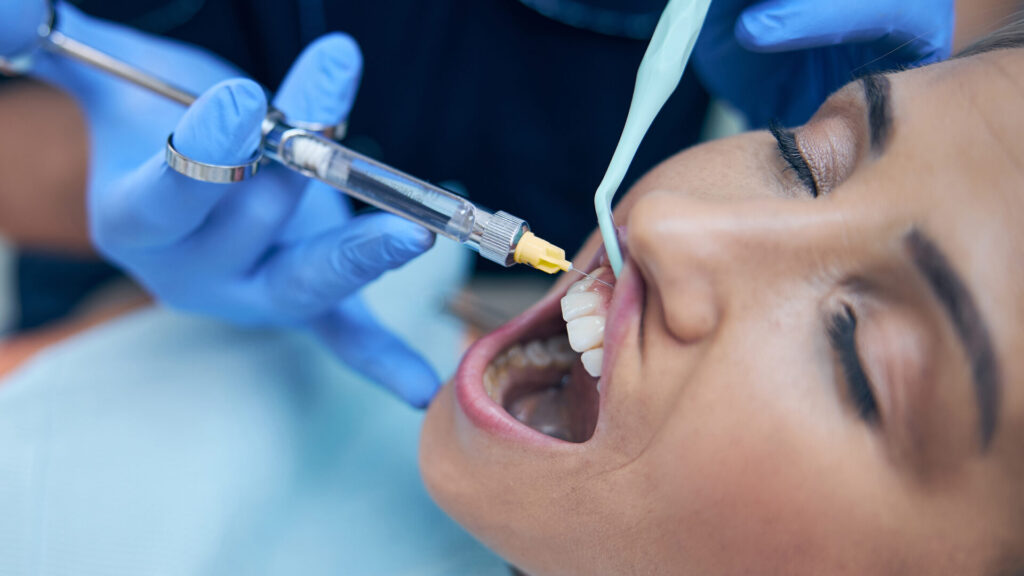
Some may need gum surgery to rectify the damage caused by periodontitis. Gingival recession treatment surgery may be an option if other measures don’t work, so think beforehand about how best you would like them handled should something happen. This can include reshaping the gums, bone grafting, or stimulating gum regeneration.
Following whatever gingival recession treatment procedure you undergo, your dentist will educate you on how to maintain gum health and, if necessary, schedule a follow-up and regular dental visits to ensure a safe recovery.
Early Periodontal Disease Detection
Periodontal disease, like most illnesses, is best treated in its early stages, so early detection and treatment of gingivitis is critical for success in both acute and chronic cases.
Avoid gum disease with proper and consistent dental hygiene. This includes the following:
- Regular visits to the dentist
- Use fluoride toothpaste twice a day
- Eating a well-balanced diet to achieve and maintain good dental health
- Lifestyle changes like giving up smoking
- Flossing your teeth daily
Gum disease is a serious problem that, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss and other health problems. However, it’s important to note that gum disease is still reversible in its early stages.
If you have any symptoms of gum disease, such as gums that are red, swollen, and bleed easily, please contact TEETH @ Tiong Bahru today for a consultation in Singapore for gingivitis treatment. We can help you get your oral health back on track and with gum disease treatment to prevent the progression. Contact us if you think you might be suffering from this condition.