Understanding Teeth Clenching (Bruxism)
Teeth clenching, also known as bruxism, is a medical condition characterised by the tightening of the jaw muscles, which press the upper and lower teeth together.
Clenching involves holding the upper and lower teeth tightly together without movement, whereas grinding is a back-and-forth motion of the teeth, often accompanied by a distinct sound. Both can put excessive pressure on the jaw, leading to jaw pain, severe tooth wear, and even tooth fractures.
You can be unconsciously clenching your teeth during the day, or at night while sleeping. In either case, whether you are clenching your teeth when awake or clenching your teeth at night, it is usually a subconscious response to stress. Globally, more than one in five people experience some form of bruxism, including in Singapore.
Early recognition is important because clenching can lead to tooth fractures, enamel wear, jaw pain, headaches, and even long-term jaw joint disorders if left unaddressed.
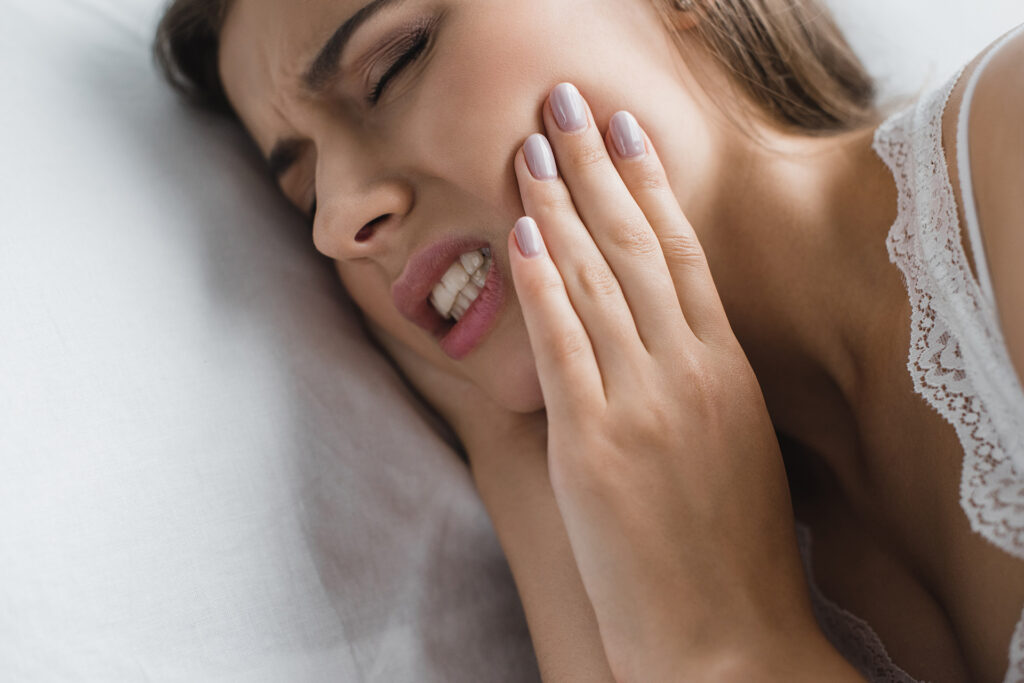

Causes and Risk Factors
Clenching teeth can be caused by many factors. Emotional stress and anxiety are the most common triggers, especially in high-pressure environments where concentration is intense and demanding. Medically, jaw misalignment, temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD) and certain neurological conditions can increase the risk of bruxism. Sleep-related issues like obstructive sleep apnea or disrupted sleep cycles can also be linked to nighttime clenching.
Substances like caffeine, alcohol, nicotine and even certain antidepressants can contribute. There is also a genetic component, as bruxism can sometimes run in families.
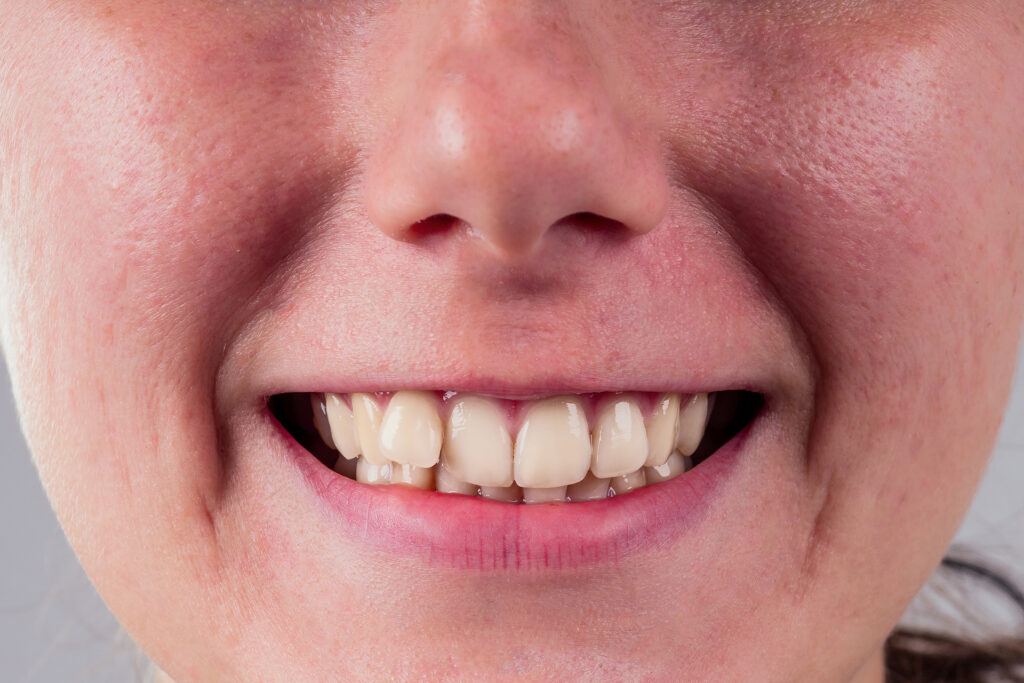

Signs and Symptoms
Common signs of clenching are a tight, fatigued jaw upon waking or stiffness during the day. Morning headaches, temple pain and earaches are also common. Over time, patients may notice worn, chipped or cracked teeth, as well as increased tooth sensitivity.
Disturbed sleep and resulting daytime fatigue are also signs that clenching occurs while asleep.
Effects on Oral and General Health
Repeated pressure from clenching can wear down the enamel of the teeth, exposing the sensitive dentin beneath. Repeated clenching can also change the biting surface of the teeth, leading to abnormal wear and negatively affecting dental function. This leads to both increased sensitivity and a higher risk of tooth decay. Severe or prolonged clenching can fracture teeth, loosen them, and, in extreme cases, lead to gum recession.
Stress on the temporomandibular joints can cause inflammation, restricted movement or chronic jaw pain. In some patients, the secondary effects of clenching teeth can extend to neck and shoulder tension due to the interconnectedness of the muscles.

Gum Disease Prevention
Gum disease is a common and often overlooked complication of teeth clenching and grinding. The constant grinding habit can irritate and inflame the gums, increasing the risk of gum disease and, in severe cases, tooth loss.
A dentist can also recommend a mouth guard or other dental correction to minimise the impact of bruxism on your gums and teeth. They can also work with you to try to deduce the cause of your teeth clenching. By being proactive and addressing the root causes of clenching, you can help preserve your gums and prevent long-term dental issues.
Diagnosis of Teeth Clenching
At TEETH @ Tiong Bahru, our dentists diagnose bruxism through a combination of clinical examination, patient history and observation of tooth wear patterns. Our dentists may also assess jaw alignment and muscle tenderness. Imaging techniques, such as X-rays or CBCT scans, can help evaluate structural damage. In some cases, a sleep study may be conducted when nocturnal bruxism is suspected.
How to Stop Clenching Teeth During the Day
To stop clenching your teeth during the day, build awareness of the habit and consciously keep your teeth slightly apart with your lips closed. Relax your jaw and facial muscles, take regular posture and breathing breaks, and limit stimulants like caffeine that can increase muscle tension. Setting phone reminders or using sticky notes as ‘jaw check’ prompts can help while you get yourself into the habit of relaxing your jaw.
Good posture reduces strain on the jaw, particularly for individuals who spend a lot of time at desks. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, breathing exercises, and regular breaks, can also be effective in helping you reduce teeth clenching during the day. For severe cases, dentists may recommend thin, discreet bite guards designed for daytime use.
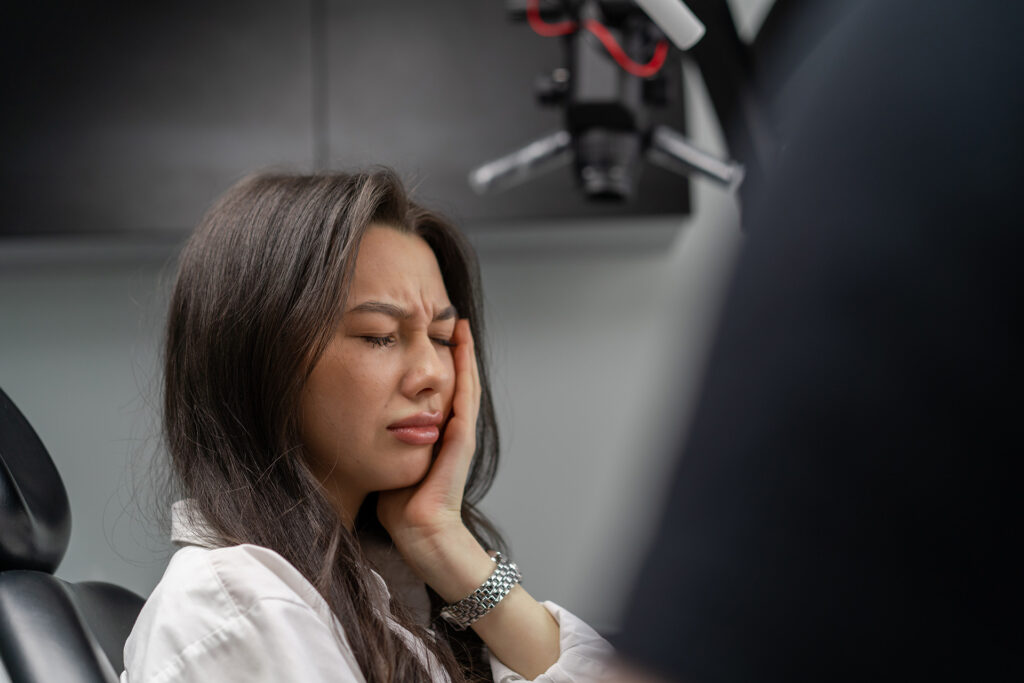

How to Stop Clenching Teeth in Sleep
To prevent clenching your teeth during sleep, consider wearing a custom night guard to protect your teeth. Enhance your sleep routine by establishing a consistent bedtime and incorporating relaxation techniques to promote a restful night’s sleep. Avoid caffeine and alcohol in the evening to reduce stress factors while you sleep. Diagnose and treat any underlying sleep disorders with the help of a specialist. Additionally, perform gentle jaw stretches before bed to relax the muscles.
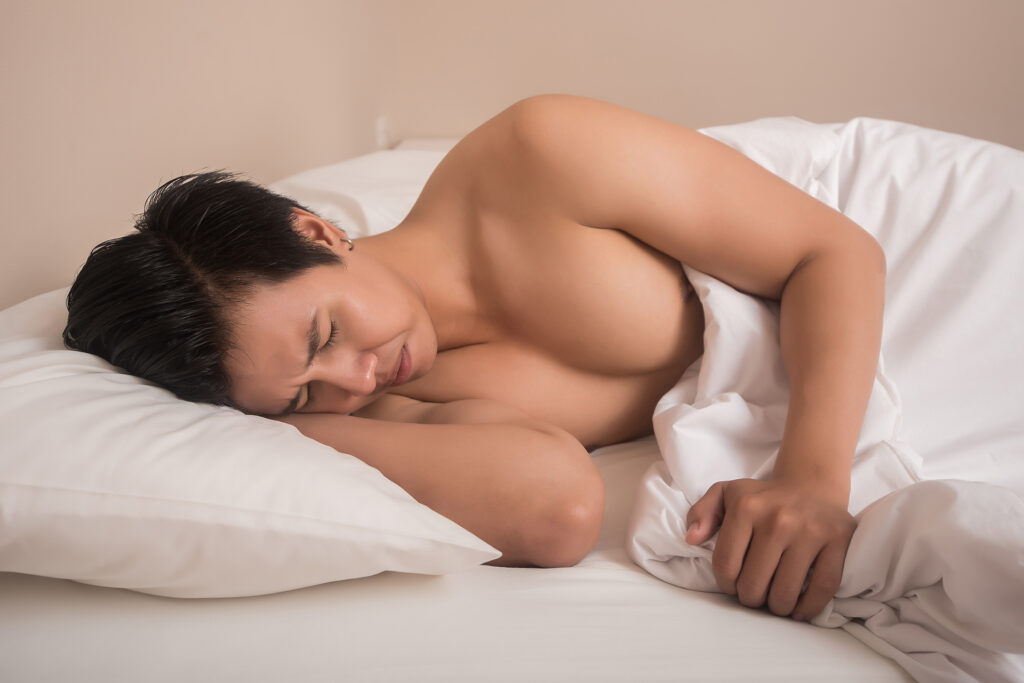

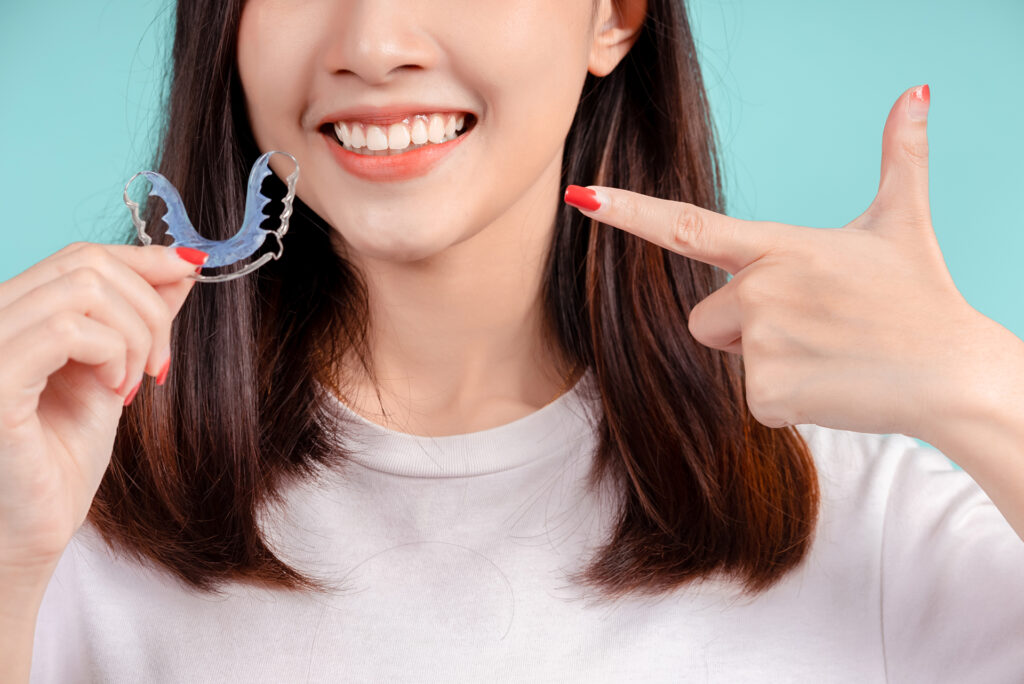
Treatment and Professional Management
Professional care for bruxism often begins with custom-made occlusal splints or night guards, tailored for comfort and maximum protection. These interventions are designed to alleviate symptoms and prevent further dental damage.
Jaw physiotherapy, massage and targeted stretching relieve muscle tension. Stress-reduction programmes and cognitive-behavioural therapy address psychological triggers. For severe and persistent cases, Botox injections into the jaw muscles may be considered to limit overactivity temporarily. Multidisciplinary care, involving dentists, physiotherapists and sleep specialists, ensures comprehensive management of both grinding and clenching behaviours.

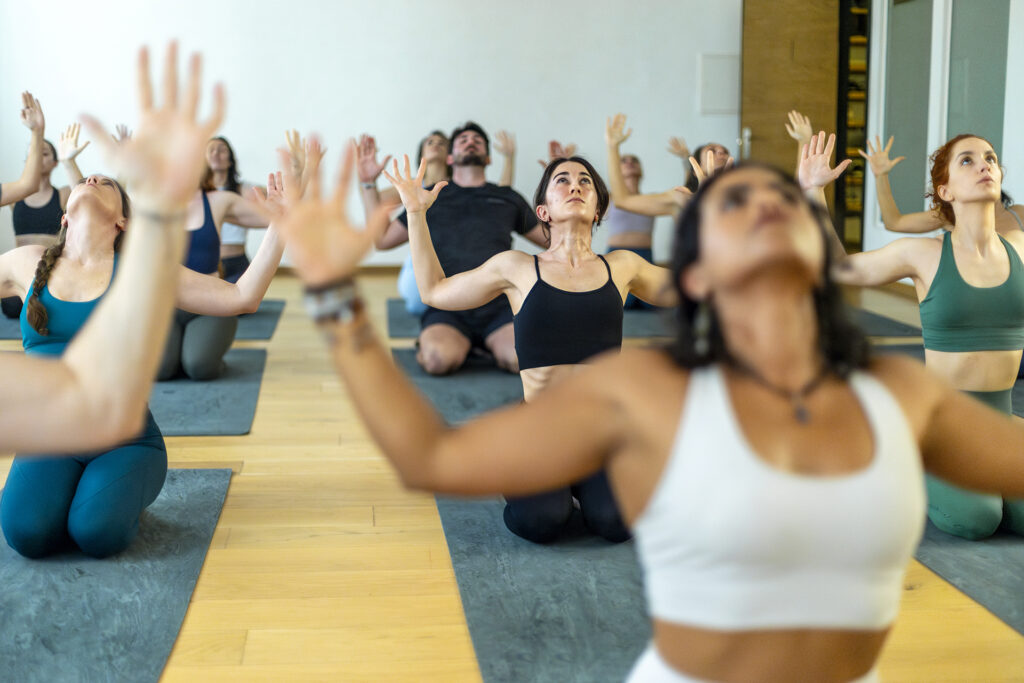
Alternative Therapies for Bruxism
In addition to traditional treatments such as mouthguards and dental corrections, some people find relief through alternative therapies. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga or deep breathing exercises, can help manage emotional stress, which is a common trigger for teeth grinding and clenching. Other approaches, like acupuncture or hypnotherapy, may also work for some people in reducing bruxism.
Lifestyle changes also play a significant role. Avoiding chewing gum, limiting alcohol consumption and being mindful not to clench your teeth during the day can all help reduce the risk of dental problems associated with bruxism. Before starting any alternative therapy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or dentist to ensure the approach is safe and suitable for your needs.

Teeth Clenching in Children
Children can also experience bruxism, often due to stress, dental misalignment or airway issues during sleep. Signs may include tooth wear, morning jaw discomfort, disrupted sleep and tooth pain. Early dental assessments are crucial in preventing long-term effects. Treatment may involve habit awareness, addressing underlying airway issues or providing protective bite guards. If your child tells you that their teeth hurt in the morning, it’s a good idea to bring them to the dentist to check on teeth clenching or grinding.
FAQs about Teeth Clenching
Can clenching teeth cause ear problems or tinnitus?
Why do I clench my teeth more when exercising or lifting weights?
Can teeth clenching affect facial appearance over time?
Is clenching teeth linked to digestive or airway issues?
Can bruxism affect dental implant success?
Why do I only clench on one side?
Protect Your Smile Today
Teeth clenching may seem harmless at first, but over time it can cause serious damage to teeth, gums and jaw health. You can protect your smile and avoid long-term complications with professional help.
If you experience jaw pain, worn teeth or headaches that may be related to teeth clenching, the team at TEETH @ Tiong Bahru can help you with a thorough assessment and a personalised treatment plan. From custom bite guards to stress management strategies, we are here to help you preserve your oral health and comfort. If you want to learn how to stop clenching your teeth, contact TEETH @ Tiong Bahru today to book your appointment and start breaking the cycle.