Healthy gums are the foundation of a strong, confident smile. The gum tissue acts as a barrier, protecting the roots of your teeth and the underlying bone from bacteria and physical damage. When this protective tissue starts to recede, it exposes the tooth roots, increasing the risk of sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss.
Across the world, including Singapore, receding gums are a common oral health issue. Many people don’t realise there’s a problem until it becomes visible or painful. Knowing what causes receding gums, identifying early signs and knowing your options for receding gums treatment can help you take control of your gum health and prevent further complications. To protect your oral health, you need to recognise the symptoms and treatment options so you can act fast if you suspect your gums are receding.
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession often develops silently, without pain, which is why regular dental check-ups are crucial. Early signs of receding gums include tooth sensitivity, longer-looking teeth, visible roots and changes in the gum line. Swollen, red or bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing, are warning signs that should not be ignored. Persistent bad breath and bad taste in the mouth may also indicate underlying gum problems.
Fortunately, there are effective receding gum treatments. These include non-surgical procedures, such as scaling and root planing, as well as surgical approaches, like gum grafting, along with lifestyle changes to support gum health.
Knowing the causes and catching symptoms early can make all the difference. By prioritising oral hygiene and scheduling regular dental visits, you can prevent gum recession and have healthy teeth and gums for life.
What Causes Receding Gums?
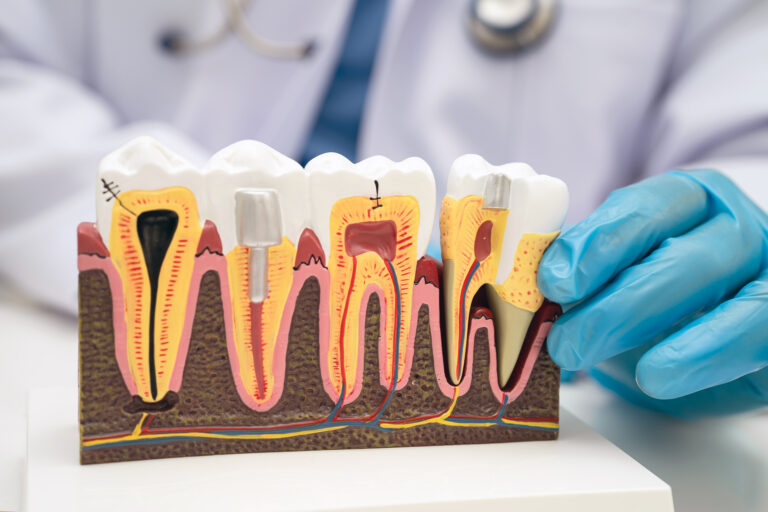
Several factors can cause receding gums, and it’s often a combination of issues that leads to gum recession. The most common factor is gum disease, which begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, resulting from poor oral hygiene. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, which can lead to gum inflammation known as gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease that destroys gum tissue and bone. As the gums pull away from the teeth, pockets form where bacteria can thrive, exacerbating the condition.
Other causes include:
- Aggressive brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear away gum tissue. It’s a common misconception that brushing harder cleans better. In reality, it can cause damage over time.
- Poor oral hygiene is another contributor. Not brushing and flossing regularly allows plaque to build up along the gum line, increasing the risk of inflammation and infection.
- Tobacco use, whether smoking or chewing, has also been linked to gum recession due to reduced blood flow to the gums.
- Hormonal changes, especially in women during pregnancy, menopause or menstruation, can make gums more sensitive and prone to recession.
- Genetics also play a role. Some people are genetically more susceptible to gum disease and recession.
- Clenching or grinding your teeth (bruxism) and misaligned teeth puts extra force on the gums and can also cause gum recession.
If you notice that your gums are receding, it is essential to identify the underlying cause early to prevent further damage and to protect your oral health.
Receding Gums Treatment
The treatment for receding gums depends on the underlying cause and extent of gum loss. In the early stages, scaling and root planing, as well as the non-invasive solutions listed below, may be recommended:
| Non-Surgical Treatments | About the Treatment |
| Improved Oral Hygiene Practices | Emphasising proper brushing and flossing techniques to prevent further gum recession |
| Desensitizing Agents | Used to alleviate tooth sensitivity associated with exposed roots |
| Orthodontics | Correcting misaligned teeth to reduce stress on gums and prevent recession |
| Dental Bonding | Applying resin to cover exposed roots and improve appearance |
| Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing) | Removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line to treat gum disease |
| Topical Antibiotics | Applying antibiotics directly to the gums to combat bacterial infections |
| Medications | Using antiseptic chips, antimicrobial mouthwash and enzyme suppressants to reduce bacteria and inflammation |
For more advanced cases of gum recession, surgical options may be necessary.
| Surgical Options | About the Treatment |
| Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation | A minimally invasive procedure that restores gum tissue without grafts or sutures |
| Gum Grafting | Transplanting tissue to cover exposed roots and restore the gum line |
Other treatments may include regenerative procedures that stimulate bone and tissue re-growth, as well as composite resins to cover exposed roots to enhance aesthetics. Timely treatment is key to preventing further damage or complications. With prompt and proper care, you may be able to stop or even reverse the gum recession process. Your dentist will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Home Remedies for Receding Gums
While professional dental care is necessary for managing gum recession, there are also home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and promote gum health. Using a soft toothbrush and brushing gently can protect delicate gum tissue from further damage. Adding an antimicrobial mouthwash to your daily routine can reduce bacteria and inflammation in the gums.
Some people find that oil pulling with coconut oil helps with gum health as it may reduce harmful bacteria in the mouth. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C, supports the repair and maintenance of gum tissue.
Flossing and good oral hygiene are key to healthy gums. If you have tooth sensitivity due to receding gums, using a desensitising toothpaste can help. Always consult your dentist before trying any new home remedies to ensure they are suitable for you and to avoid harm.
How to Prevent Receding Gums
Preventing receding gums starts with good oral hygiene. Brushing twice a day with a soft toothbrush and gentle circular motions can help prevent gum damage. Flossing daily removes plaque from areas that brushing can’t reach.
Quitting smoking and staying away from tobacco products can lower your risk of gum recession and other oral health issues. A diet rich in vitamins C and D supports gum health and the tissues that hold your teeth. Managing stress is also essential, as high stress can cause teeth grinding and negatively impact oral health.
It’s also worthwhile to avoid certain foods, such as hard candies, ice, sticky foods like caramel or dried fruits, sugary foods and drinks, and acidic foods and beverages, including citrus fruits and sodas. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps rinse away food particles and bacteria, supporting healthier gums.
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for monitoring gum health and catching any early signs of gum recession or gum disease. Quitting tobacco products, managing stress (which can cause teeth grinding) and eating a healthy diet also support gum health.
If you’re not sure how to stop receding gum lines from getting worse, your dentist can give you personalised advice and show you how to brush and floss properly for your needs.
Managing Tooth Sensitivity with Special Toothpaste
Tooth sensitivity is a common result of receding gums. When the gum layer pulls back, it exposes the dentin, which contains microscopic channels leading to the tooth’s nerve. This exposure can cause discomfort when consuming hot, cold or sweet foods and drinks.
Using a toothpaste specifically designed for sensitive teeth can help manage this condition. These toothpastes contain compounds that help block the transmission of sensation from the tooth surface to the nerve. Your dentist can recommend a product that’s suitable for you and your oral health.
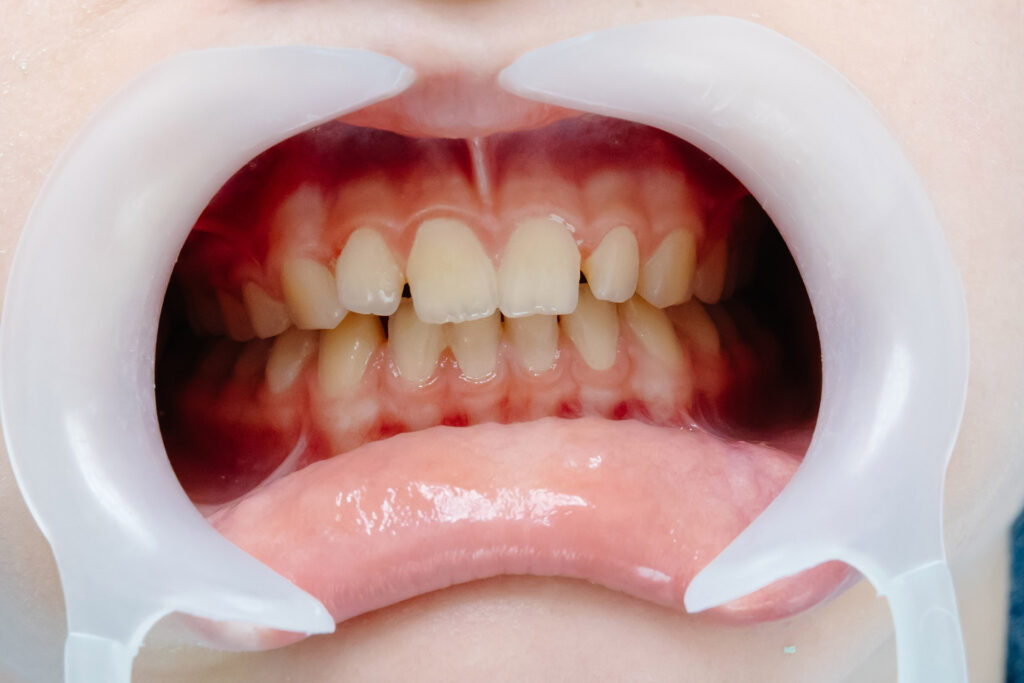
Orthodontics and Gum Recession
Orthodontic treatment, such as fixed braces or clear aligners, can impact gum health in several ways. While properly aligned teeth are easier to clean and less likely to develop plaque buildup, poorly managed orthodontic care can cause gum recession.
If you have or are considering braces and are worried about receding gums, it’s essential to work closely with both your orthodontist and general dentist. They can develop a treatment plan to ensure your gums stay healthy throughout your orthodontic journey.
Good oral hygiene is even more important during orthodontic treatment. Food particles can become trapped around brackets and wires, making brushing and flossing essential for maintaining oral health. Your dental team can also recommend tools, such as interdental brushes or water flossers, to make cleaning easier.
Can Receding Gums Fix Themselves?
While early gum inflammation can be reversed with good oral hygiene and professional cleaning, actual recession requires intervention to repair.
That’s why timely diagnosis and treatment for receding gums are key. Ignoring signs of receding gums can lead to further exposure of the tooth roots, increased sensitivity, and, ultimately, tooth loss. With proper care and treatment, you can stop the progression of gum recession and protect your long-term oral health.
Your dentist can explain how to treat receding gums based on your condition. Early intervention may involve non-surgical treatments, while more advanced cases may require grafting or other procedures to restore gum coverage.
Book an Appointment for Your Receding Gums
Receding gums are more than just a cosmetic issue. It’s a sign of gum disease. If left untreated, it can lead to undue sensitivity, aesthetic concerns and tooth loss. The good news is that with early detection, proper treatment, and preventive care, you can manage gum recession and maintain your smile.
If you’re worried about gum recession or want to know how to prevent receding gums, don’t wait for symptoms to get worse. Book an appointment with TEETH @ Tiong Bahru today to consult with our team and let us help you restore and protect your gum health.