When it comes to oral health, gum infections are something many of us overlook until the problem becomes too big to ignore. What can start as a mild irritation can escalate into full-blown gum disease and must be addressed as soon as possible to save your teeth and overall health. Discover the ins and outs of gum infections, from early signs to prevention and treatment, so you know how to protect your oral health.
What is a Gum Infection?
A gum infection occurs when bacteria accumulate along and beneath the gum line, causing inflammation, discomfort, and potentially severe complications. These infections are often linked to periodontal disease, ranging from gingivitis, a milder and reversible stage, to periodontitis, a more advanced stage that can cause permanent damage, including tooth loss and systemic health implications.
What is Periodontal Disease?
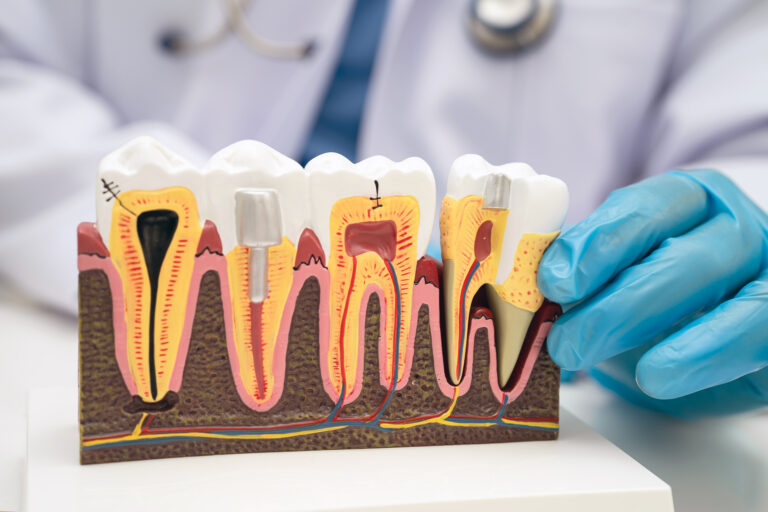
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, refers to inflammatory conditions afflicting the gums and bones supporting teeth. Periodontal disease affects millions worldwide. If left untreated, it can cause severe complications, including tooth loss and other systemic health issues. The root cause of periodontal disease is the buildup of plaque – a sticky film of bacteria – on your teeth. When plaque is not removed correctly, it can inflame the gums and cause gingivitis, the initial and reversible stage of gum disease. If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe stage of the disease, which can become irreversible.
There are several types of periodontal disease:
- Gingivitis: The mildest type of gum disease, it can be reversed through proper treatment and effective oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis: This advanced gum disease can harm the bone and tissue supporting your teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
- Aggressive Periodontitis: A rare and fast-progressing form of gum disease that can destroy the bone and tissue around the teeth quickly.
- Chronic Periodontitis: A slow-progressing form of gum disease that damages the bone and tissue around the teeth over time.
By recognising the early signs and symptoms of periodontal disease, you can get treatment on time, stop the disease from progressing, and restore your gum health.
Gum Infection Symptoms
Spotting the signs of a gum infection early can make a big difference in treatment outcomes. Key gum infection symptoms to look out for include:
- Inflamed and Tender Gums: Redness around the gums is one of the first signs of an infection. Swollen gums are also infection symptoms.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed when you brush or floss should not be ignored, as this can be a sign of periodontal disease.
- Bad Breath: A foul taste or smell in your mouth can indicate underlying issues.
- Receding Gums: If the gum line is noticeably pulling away from the teeth, this is a warning sign for periodontal disease.
- Pain and Sensitivity: Gum infection pain is most noticeable when eating or brushing.
- Pus Formation: Abscesses or visible discharge means a severe gum infection.
- Loose Teeth: Tooth stability or alignment changes are a late-stage warning sign of periodontal disease and possibly periodontitis
If you see these signs, visit a TEETH @ Tiong Bahru dentist soon to prevent further complications.
How Do You Get a Gum Infection?
Understanding the causes of gum infections is essential for prevention. The primary offender is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that develops on your teeth and gums. If not adequately removed, plaque can harden into tartar, which requires professional cleaning for removal. The bacteria in both plaque and tartar irritate the gums, leading to infection.
These are several factors that affect the negative effects of plaque and tartar:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly allows bacteria to grow, and plaque to develop.
- Smoking: Tobacco products increase the risk of a gum disease infection.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and menopause can make gums more sensitive.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes weaken the immune system and make gums more vulnerable.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications can reduce saliva flow and exacerbate plaque buildup.
- Poor Diet: Too much sugar and processed food both feed the bacteria of plaque and tartar.
Consequences of Untreated Gum Disease
Untreated gum disease can lead to a multitude of other conditions that can have a dire effect on your oral health and beyond. One of the most immediate consequences is tooth loss, as the disease can make your teeth loose and eventually fall out. Other consequences of untreated gum disease include:
- Bad Breath: Bad breath can be embarrassing and a sign of underlying gum problems.
- Pain and Discomfort: Gum disease can be harrowing for the mouth, especially when eating or drinking hot or cold food.
- Difficulty Chewing and Swallowing: As your teeth become loose, chewing and swallowing can be difficult, affecting your nutrition and quality of life.
- Changes in Facial Shape: Bone loss from gum disease can cause changes in the shape of your face and jaw.
As mentioned, gum disease affects more than just oral health. Studies have established a connection between gum health and systemic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and complications during pregnancy. Even minor gum problems should be treated quickly, as neglecting them can result in more significant health issues. Maintaining proper oral hygiene and scheduling regular dental check-ups can help prevent gum disease and its related health risks.
Managing and Treating Gum Disease
Gum infections can only be managed with professional intervention and regular oral care. Depending on the severity, your dentist may recommend different methods to treat gum disease.
Scaling and polishing are two of the most likely and effective treatments, depending on the stage of periodontal disease. This deep cleaning by a dental professional removes plaque and tartar below the gum line, reduces the bacterial presence, and allows healing. A part of this process is ‘root planing’, which removes tough tartar and bacterial deposits from the roots of the teeth.
Your dentist may also suggest other treatments, depending on the scale of the gum infection:
- Medications: Antibiotics, topical or oral, can remove the infection.
- Surgical Interventions: Advanced infections may require flap surgery to clean deeper pockets or grafting to replace gum tissue.
- Bone Grafts: Used for advanced periodontal disease, bone grafts replace lost bone and allow healthy bone tissue to regrow over time.
- Gum Surgery: Flap surgery cleans out stubborn tartar in gum pockets and restores gum tissue around the teeth for healing.
- Bone Grafting: This procedure involves placing bone grafting material in areas of bone erosion to provide a scaffold for the patient’s bone to regrow over time.
Preventing Gum Disease
Gum infections can be prevented. You can practice good oral hygiene at home by brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove food particles and plaque, and gargling with an antibacterial mouthwash to add extra protection. Also, eating a diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins and minimising the consumption of sugary and processed food can go a long way toward keeping your gums healthy.
Importantly, schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings to stay ahead of potential problems. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and advise you on improving your oral care routine.
When to See a Dentist
If you have persistent gum infection pain, or swelling, do not delay seeking professional care. Early intervention is key to stopping gum disease and preventing long-term consequences.
At TEETH @ Tiong Bahru, we specialise in diagnosing and treating gum infections, offering personalised care tailored to your unique needs. Don’t wait for gum discomfort to escalate. Contact TEETH @ Tiong Bahru today to book an appointment.